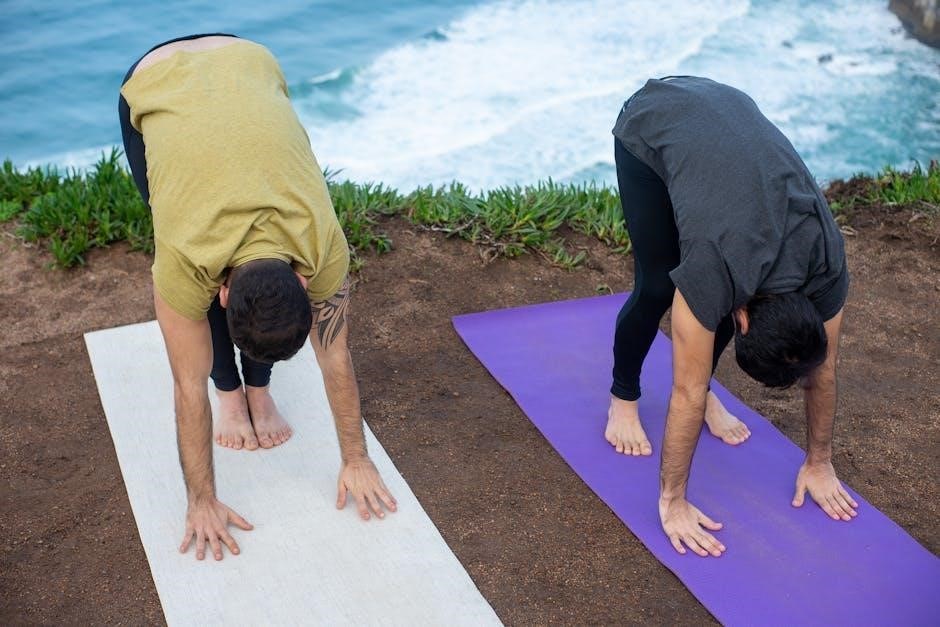
This comprehensive guide serves as a roadmap for understanding physical therapy practices‚ emphasizing evidence-based approaches and practical insights for clinicians‚ students‚ and professionals seeking to enhance patient care effectively.
1.1 Overview of Physical Therapy Practice
Physical therapy practice focuses on enhancing movement‚ function‚ and overall well-being through evidence-based interventions. It involves assessing patients’ conditions‚ developing personalized treatment plans‚ and implementing therapies to address impairments. Physical therapists work in various settings‚ including hospitals‚ clinics‚ and private practices‚ to improve mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and promote health. The practice integrates manual techniques‚ exercises‚ and education to empower patients‚ emphasizing a patient-centered approach for optimal outcomes and long-term success in rehabilitation and preventive care.
1.2 Importance of Evidence-Based Practice in Physical Therapy
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is crucial for delivering effective and safe physical therapy care. It integrates clinical expertise with scientific evidence and patient values to guide decision-making. EBP ensures treatments are grounded in the best available research‚ improving patient outcomes and reducing variability in care. By formulating specific questions and seeking evidence-based answers‚ physical therapists enhance their practice‚ ensuring interventions are current‚ effective‚ and tailored to individual needs‚ fostering continuous improvement and accountability in the field.

Key Components of Physical Therapy Practice
Effective physical therapy practice hinges on evidence-based interventions‚ strong communication‚ and keen observation skills to deliver personalized‚ patient-centered care‚ ensuring optimal outcomes and continuous improvement in treatment approaches.
2.1 Formulating Specific Questions for Effective Practice
Formulating specific questions in physical therapy practice is crucial for guiding evidence-based decisions. These questions should be clear‚ focused‚ and actionable‚ enabling therapists to identify the most effective interventions‚ address patient needs‚ and ensure scientific validity. By framing queries that can be scientifically investigated‚ professionals can enhance treatment outcomes‚ personalize care‚ and stay updated with best practices‚ fostering continuous improvement in patient management and clinical success.
2.2 Communication Skills for Physical Therapists
Effective communication is vital for building trust and ensuring patient understanding in physical therapy. Verbal and nonverbal cues‚ including active listening and empathy‚ foster a supportive environment. Clear explanations of treatments and expectations help patients engage actively in their care. Strong communication skills also facilitate collaboration with other healthcare professionals‚ enhancing overall patient outcomes and satisfaction. Developing these skills is essential for therapists to convey confidence‚ clarity‚ and compassion‚ ensuring successful treatment and patient-centered care.
2.3 The Role of Observation in Physical Therapy
Observation is a critical tool in physical therapy‚ enabling therapists to assess patient movements‚ behaviors‚ and responses to treatment. It allows for a deeper understanding of a patient’s condition and progress‚ aiding in accurate diagnosis and personalized care. Observation also helps therapists refine their techniques and engage patients more effectively. Additionally‚ it provides insights into the profession for students and newcomers‚ helping them determine if physical therapy aligns with their career aspirations and skills.
Starting a Physical Therapy Practice
Starting a physical therapy practice involves developing a business plan‚ securing a prime location‚ and implementing effective marketing strategies to attract patients and ensure long-term success.
3.1 Developing a Business Plan for a Cash-Based Practice
A well-structured business plan is essential for launching a cash-based physical therapy practice. It should include market analysis‚ target audience identification‚ financial projections‚ and marketing strategies. Define your mission‚ vision‚ and unique selling points to differentiate your practice. Outline operational logistics‚ such as staffing‚ equipment‚ and location. Establish clear revenue goals and expense management plans. A solid business plan ensures sustainability and growth‚ guiding your practice toward long-term success in a competitive healthcare landscape.
3.2 Finding the Right Location and Patients
Selecting the right location for your physical therapy practice is crucial for accessibility and visibility. Assess factors like foot traffic‚ parking‚ and competition. Identify your target patient demographic‚ such as athletes or geriatric populations‚ to tailor services. Use online tools and community outreach to attract patients. Building relationships with local healthcare providers and engaging in community events can enhance visibility. Ensure your location aligns with your practice’s mission and patient needs for optimal growth and reach.
3.3 Marketing Strategies for Success
Effective marketing is essential for attracting patients and growing your practice. Develop a strong online presence through SEO and social media engagement. Utilize email marketing and content creation to educate potential patients. Host community events and workshops to build trust and visibility. Partner with local healthcare providers for referrals. Track marketing metrics to refine strategies and ensure optimal ROI. A well-executed marketing plan can differentiate your practice and drive long-term success in a competitive market.
Coding and Payment Guide for Physical Therapists
This section provides detailed insights into coding and billing practices‚ payment models‚ and reimbursement strategies‚ ensuring compliance and financial stability for physical therapy practices.
4.1 Understanding Coding and Billing Practices
Accurate coding and billing are crucial for physical therapy practices to ensure proper reimbursement and compliance. This section covers the essentials of CPT codes‚ ICD-10‚ and billing procedures. It emphasizes staying updated on coding changes and understanding payer-specific requirements. Proper documentation and compliance with regulatory standards are highlighted to avoid errors and audits. Resources like the Coding and Payment Guide provide detailed instructions‚ ensuring therapists can navigate the complexities of billing effectively and maintain financial stability in their practice.
4.2 Navigating Payment Models and Reimbursement
Understanding payment models and reimbursement strategies is vital for sustainable physical therapy practice. This section explores fee-for-service‚ value-based care‚ and bundled payment systems. It highlights the importance of understanding reimbursement rates‚ payer policies‚ and contract negotiations. Staying informed about regulatory changes and utilizing resources like payment guides ensures compliance and maximizes revenue. Effective reimbursement strategies help therapists deliver high-quality care while maintaining financial stability in an evolving healthcare landscape.
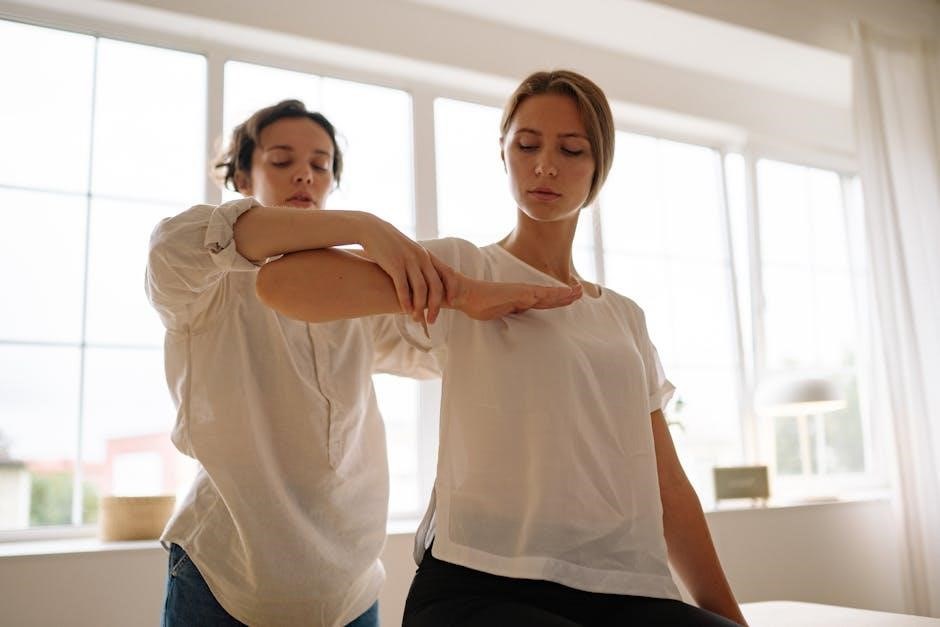

Documentation in Physical Therapy
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is essential for tracking patient progress‚ ensuring compliance‚ and maintaining clear communication. It forms the foundation of effective patient care and legal standards.
5.1 SOAP Notes: Structure and Best Practices
SOAP notes provide a structured method for documenting patient interactions‚ consisting of Subjective‚ Objective‚ Assessment‚ and Plan sections. They ensure clarity‚ consistency‚ and thoroughness in patient records. The Subjective section captures patient-reported symptoms and concerns‚ while the Objective section details measurable observations and test results. The Assessment synthesizes this information to formulate a diagnosis or progress update. Finally‚ the Plan outlines the next steps in treatment‚ including interventions‚ patient education‚ and follow-up care. Accurate and timely SOAP notes are essential for effective communication‚ continuity of care‚ and legal compliance‚ serving as a critical tool in physical therapy practice.
5.2 Confidentiality and Handling Patient Information
Confidentiality is a cornerstone of ethical physical therapy practice‚ ensuring patient trust and compliance with legal standards like HIPAA. Physical therapists must safeguard patient records‚ securing them against unauthorized access. Best practices include storing files securely‚ limiting access to authorized personnel‚ and using encrypted digital systems. Training staff on confidentiality protocols is essential‚ as is obtaining patient consent before sharing information. Transparent communication about data usage fosters trust‚ while breaches can lead to legal consequences and reputational damage;
Advanced Techniques in Physical Therapy
Advanced techniques include biofeedback‚ enhancing mind-body connection‚ and deliberate practice‚ fostering continuous improvement in patient care and therapeutic outcomes through focused‚ evidence-based methodologies.
6.1 Biofeedback: Enhancing Mind-Body Connection
Biofeedback is a mind-body technique that equips patients with tools to control physiological functions like heart rate and muscle tension. By using specialized equipment‚ individuals gain awareness of their body’s responses‚ enabling them to self-regulate through conscious adjustments. This method is particularly effective in managing chronic pain‚ stress‚ and rehabilitation processes‚ promoting a holistic approach to recovery and overall well-being by integrating both physical and mental practices.
6.2 Deliberate Practice for Continuous Improvement
Deliberate practice is a systematic approach to skill refinement‚ focusing on targeted exercises with feedback to enhance performance. It involves breaking tasks into components‚ repeating challenging areas‚ and adjusting techniques based on outcomes. This method accelerates progress‚ fosters mastery‚ and ensures continuous improvement in physical therapy‚ helping therapists refine their expertise and deliver optimal patient care effectively over time with consistent effort and dedication to professional growth.

Finding the Right Physical Therapy Clinic
Use clinic finder tools to locate facilities near you‚ ensuring they offer the services you need and operate at convenient times‚ making it easier to prioritize your care.
7.1 Using Clinic Finder Tools
Clinic finder tools simplify locating physical therapy services near you. Enter your location or postcode to search for clinics‚ filter by services offered‚ and view operating hours. These tools often provide reviews‚ helping you assess quality and patient satisfaction. Ensure the clinic meets your specific needs‚ such as specialized therapies or equipment. Using these resources saves time and helps you make informed decisions about your care.
7.2 Evaluating Clinic Services and Availability
Evaluate clinics by reviewing their services‚ therapist expertise‚ and availability. Check if they offer specialized therapies or equipment suited to your needs. Consider clinic hours and patient load to ensure timely care. Read reviews and ask about success rates or patient satisfaction. Ensure the clinic aligns with your specific requirements‚ such as insurance acceptance or bilingual staff. This thorough assessment helps you make an informed decision and choose a clinic that meets your expectations for effective treatment.
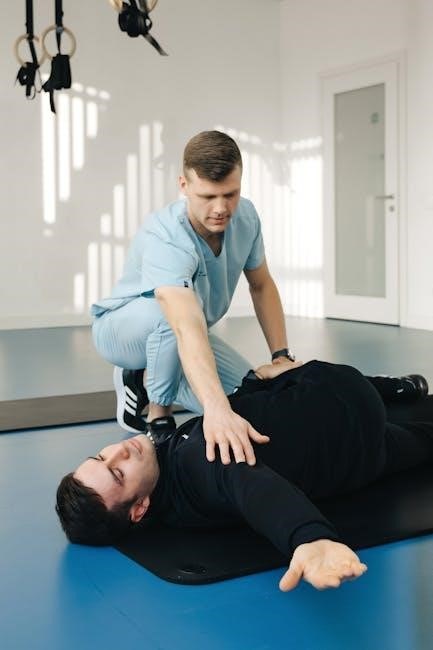
Understanding Physical Therapy Treatments
Physical therapy treatments focus on improving mobility‚ strength‚ and function. Therapists use exercises‚ manual techniques‚ and modalities to address injuries‚ manage pain‚ and enhance overall well-being effectively.
8.1 What to Expect from Physical Therapy Sessions
Physical therapy sessions typically begin with a thorough assessment to identify specific needs and goals. Patients can expect personalized exercises‚ manual therapy‚ and modalities like heat or cold therapy. Sessions may also include education on proper posture‚ movement techniques‚ and home exercises to enhance recovery. The therapist will monitor progress‚ adjust treatments as needed‚ and ensure active patient participation. Open communication is key to achieving optimal outcomes and addressing any concerns during therapy.
8.2 The Role of Physical Therapists in Different Settings
Physical therapists work in diverse settings‚ including hospitals‚ outpatient clinics‚ schools‚ and home health care. In hospitals‚ they focus on acute care‚ helping patients recover from surgeries or injuries. In outpatient settings‚ they specialize in rehabilitation and chronic condition management. School-based therapists support children with special needs‚ while home health therapists provide personalized care in patients’ homes. Their roles adapt to each environment‚ ensuring comprehensive and tailored care to improve mobility‚ strength‚ and overall well-being across various populations and needs.

Narrative Therapy in Physical Therapy Practice
Narrative therapy helps clients reframe their stories‚ fostering empowerment and resilience. It encourages clients to explore their experiences‚ identify strengths‚ and create meaningful change in their lives.
9.1 Approach and Goals of Narrative Therapy
Narrative therapy is a client-centered approach that empowers individuals to reframe their stories and challenges. It aims to help clients identify their strengths‚ resilience‚ and unique perspectives‚ fostering personal growth and meaningful change. By externalizing problems‚ individuals can gain new insights and develop alternative narratives that promote healing and self-awareness. The goal is to create a collaborative space where clients feel heard and supported in their journey toward empowerment and improved well-being.
9.2 Effective Questioning Techniques for Client Engagement
Effective questioning in narrative therapy involves asking open-ended‚ exploratory questions that encourage clients to reflect deeply on their experiences. Active listening and empathetic responses help build trust and engagement. By posing questions that challenge clients to explore their values and aspirations‚ therapists empower them to uncover new insights and perspectives. This collaborative approach fosters a deeper understanding of their stories‚ enabling clients to identify personal strengths and develop meaningful solutions to their challenges.

